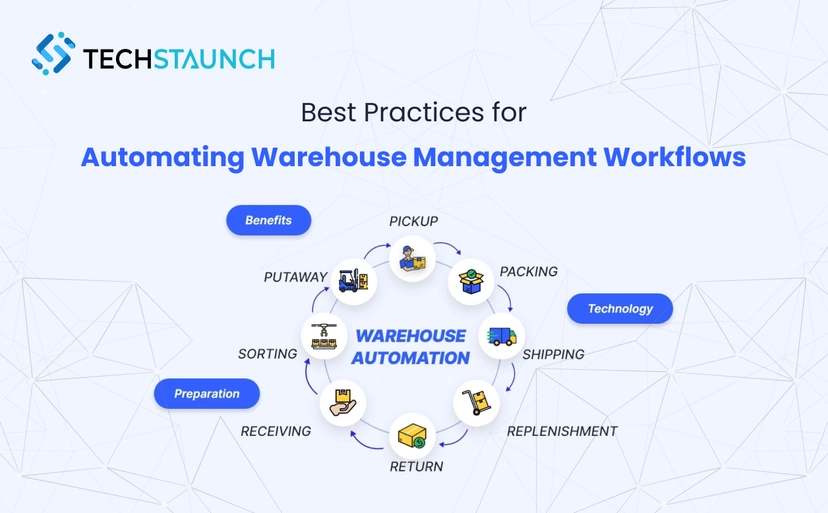
Warehouse management workflow optimization
In 2026, every warehouse manager faces identical pressures: customers demanding same-day delivery, labor shortages creating operational gaps, inventory complexity multiplying daily, and profit margins shrinking relentlessly.
Warehouse management workflows hold the answer, when automated strategically. But the most successful operations leaders aren't asking "How much can we automate?" They're asking "What exactly is a warehouse management workflow, which workflows need automation, and how do we implement without disrupting operations?"
Across North America and Europe, warehouses thriving with automation share one approach: they start with workflow understanding, not technology trends.
A 200,000 square foot distribution center in Ohio reduced order fulfillment time by 47%, not because they deployed the most expensive warehouse management system, but because they spent three weeks mapping their warehouse management workflows, identified six redundant steps, and eliminated them before implementing automation.
This complete guide answers every question about warehouse management workflows, from basic definitions to advanced automation strategies.
What is Warehouse Management Workflow? (Definition & Complete Explanation)
A warehouse management workflow is the systematic sequence of activities, processes, and tasks that govern how goods move through a warehouse facility from initial receiving through final shipping. These workflows define who does what, when, where, and how throughout the entire warehouse operation lifecycle.
Think of warehouse workflow as the operational DNA of your facility. It's the repeatable pattern of steps that transforms inbound shipments into outbound customer deliveries while maintaining inventory accuracy, operational efficiency, and customer satisfaction.
Understanding Warehouse Management Workflow Components
Every warehouse management workflow consists of several fundamental components working together:
Process Sequences define the ordered steps required to complete warehouse activities. For example, a receiving workflow includes: truck arrival, dock door assignment, unloading, inspection, counting, putaway location determination, and inventory system update.
Decision Points determine workflow branching based on specific conditions. When receiving inventory, decision points include: Does quantity match purchase order? Is product quality acceptable? Where should this item be stored? Does this require special handling?
Data Flows track information movement through warehouse systems. As physical inventory moves, data flows capture location changes, quantity updates, quality inspections, and transaction timestamps.
Role Assignments specify which warehouse personnel execute each workflow step. Receiving clerks handle inbound verification, forklift operators manage putaway, pickers fulfill orders, and packers prepare shipments.
System Interactions define how warehouse management software, barcode scanners, conveyor systems, and other technology support workflow execution.
Performance Metrics measure workflow efficiency through key performance indicators like processing time, accuracy rates, and resource utilization.
According to warehouse operations research, well-designed warehouse management workflows can improve operational efficiency by 30-50% compared to unstructured, ad-hoc approaches.
Why Warehouse Management Workflows Matter
Properly designed warehouse workflows deliver measurable business value:
Warehouse management workflows eliminate guesswork about how tasks should be executed. New employees learn faster when clear workflow documentation exists. Consistency improves when everyone follows the same proven processes.
Workflows reveal bottlenecks and inefficiencies that consume time and resources. Once identified, these pain points become automation opportunities delivering significant ROI.
Inventory accuracy depends on disciplined workflow execution. When every movement follows defined procedures with verification checkpoints, inventory discrepancies decrease dramatically.
Customer satisfaction improves when warehouse workflows consistently deliver accurate orders on time. Predictable workflows create predictable customer experiences.
Our logistics software development expertise helps organizations document current workflows, identify optimization opportunities, and implement automation that transforms operational performance.
Types of Warehouse Management Workflows (Complete List)
Understanding the different types of warehouse workflows is essential for optimization and automation. Here are the core warehouse management workflows present in virtually every facility:
1. Inbound Receiving Workflows
What is the receiving workflow in warehouse management?
The receiving workflow manages how products enter your warehouse and become available inventory. This critical workflow sets the foundation for all downstream operations.
Standard Receiving Workflow Steps:
Carrier arrival and dock door assignment. Unload products from truck or container. Verify shipment against purchase order or ASN (Advanced Shipping Notice). Inspect for damage and quality issues. Count quantities and compare to shipping documentation. Apply warehouse barcodes or RFID tags for tracking. Update warehouse management system with received inventory. Generate discrepancy reports for shortages or overages. Route products to quality inspection if required. Transfer to putaway workflow.
A New Jersey pharmaceutical distributor receives 200+ shipments daily. Before optimizing their receiving workflow, processing took 45 minutes per shipment with 12% error rates. After implementing warehouse barcode scanning and automated ASN verification, receiving time dropped to 18 minutes with 2% errors.
The lesson: Receiving workflows directly impact inventory accuracy for your entire operation. Get this workflow right, and everything downstream improves.
2. Putaway and Storage Workflows
What is putaway workflow in warehouse operations?
Putaway workflow determines where received products are stored and how they reach those locations efficiently. Strategic putaway dramatically affects picking efficiency and space utilization.
Putaway Workflow Components:
Receive putaway instructions from WMS based on slotting logic. Travel to storage location using optimized path. Verify location by scanning warehouse location barcode. Place product in designated position. Scan product warehouse barcode to confirm putaway. Update WMS with new inventory location. Receive next putaway task assignment.
Putaway Workflow Strategies:
Fixed location putaway assigns specific products to permanent locations. This simplifies picking but limits flexibility and space utilization.
Random putaway stores products in any available location, maximizing space usage. Requires robust warehouse barcode systems to track inventory locations accurately.
Velocity-based putaway places fast-moving products in easily accessible locations while slower items go to less convenient spots. This reduces overall pick travel time.
Zone-based putaway dedicates warehouse areas to specific product categories, suppliers, or customers.
A Michigan automotive parts warehouse implemented velocity-based putaway workflows driven by real-time pick frequency analysis. Average pick travel distance decreased 34%, and pickers completed 28% more orders per shift.
3. Inventory Management Workflows
What are inventory management workflows in warehouses?
Inventory management workflows maintain accurate records of what products you have, where they're located, and how many units are available. These workflows include cycle counting, stock transfers, and inventory adjustments.
Cycle Counting Workflow:
WMS generates cycle count tasks based on ABC analysis or last count date. Counter receives assignment and travels to location. Scans warehouse location barcode to confirm position. Physically counts products. Enters count quantity into handheld device. System compares count to expected quantity. Variances trigger investigation workflow. Inventory records update upon approval.
Benefits of systematic cycle counting workflows:
Eliminates disruptive annual physical inventories. Identifies and corrects inventory errors continuously. Maintains 99%+ inventory accuracy. Reveals root causes of inventory discrepancies.
A Texas electronics distributor replaced annual physical inventory with automated cycle counting workflows. Inventory accuracy improved from 94% to 99.2%, and they eliminated the $180,000 annual cost of shutting down for physical inventory.
4. Order Picking Workflows
What is order picking workflow?
Order picking workflow is the process of retrieving products from warehouse storage locations to fulfill customer orders. This workflow consumes 50-60% of warehouse labor costs, making it the highest-impact automation opportunity.
Types of Warehouse Picking Workflows:
Discrete picking workflow assigns one picker to pick one complete order. Simple to understand and implement but least efficient for multi-line orders.
Batch picking workflow combines multiple orders with common SKUs, having one picker collect all units needed across orders. Reduces travel time but requires sorting step to separate orders.
Zone picking workflow divides warehouse into zones with dedicated pickers. Orders move through zones collecting items in each area. Minimizes individual picker travel but requires order consolidation.
Wave picking workflow combines orders with common characteristics like ship date, carrier, or route. Optimizes for specific cut-off times and shipping schedules.
Cluster picking workflow allows pickers to build multiple orders simultaneously using multi-bin carts, combining benefits of batch and discrete picking.
A California e-commerce fulfillment center processes orders ranging from 1 to 50 line items. Their warehouse management workflow automatically selects picking strategy based on order characteristics:
Single-item orders use discrete picking. 2-10 item orders use cluster picking with 4-order carts. Orders over 10 items use batch picking with automated sorting.
This intelligent workflow selection improved picking productivity 42% versus single-strategy approaches.
For organizations optimizing complex picking operations, our custom software development team builds intelligent workflow engines that dynamically select optimal strategies based on real-time conditions.
5. Packing and Shipping Workflows
What is the packing workflow in warehouse management?
Packing workflow prepares picked orders for shipment, ensuring products arrive safely and shipping costs stay optimized.
Packing Workflow Steps:
Receive completed pick at packing station. Verify pick accuracy through weight check or barcode scan. Select appropriate packaging based on product dimensions. Pack items with protective materials. Apply packing slip and shipping label. Scan shipping label barcode to confirm shipment. Route to appropriate shipping dock based on carrier. Generate manifest and close shipment.
Shipping Workflow Automation:
Automated carton selection systems recommend optimal box sizes. Integrated scales verify order weight matches expected weight. Automated manifesting generates carrier documentation. Real-time tracking updates flow to customers automatically.
A Florida consumer goods distributor implemented automated packing workflows with carton selection and weight verification. Shipping cost decreased 11% through optimal box sizing, and mis-ships dropped 87%.
6. Returns and Reverse Logistics Workflows
What is returns workflow in warehouse operations?
Returns workflow manages products coming back from customers, determining disposition and returning items to available inventory when appropriate.
Returns Workflow Process:
Receive returned product from carrier. Identify order and reason for return. Inspect product condition. Make disposition decision: Resell as new. Refurbish and resell as used. Liquidate through discount channel. Dispose or recycle if unsellable. Update inventory if returning to stock. Process customer refund or exchange. Analyze return reasons for quality trends.
A Minnesota outdoor equipment retailer receives 8% of orders as returns. Before structuring their returns workflow, returned items sat in holding areas for weeks, tying up capital. After implementing automated returns workflow with immediate disposition decisions, 73% of returns returned to sellable inventory within 24 hours.
7. Replenishment Workflows
What is warehouse replenishment workflow?
Replenishment workflow moves products from bulk storage locations to forward picking locations, ensuring pickers always have accessible inventory.
Replenishment Workflow Types:
Min/max replenishment triggers when pick location quantity falls below minimum threshold, bringing inventory to maximum level.
Demand-based replenishment forecasts pick requirements and replenishes proactively before stockouts occur.
Wave replenishment coordinates with pick waves, ensuring inventory availability before pickers arrive.
An Illinois industrial distributor implemented automated replenishment workflows that analyze upcoming pick requirements and generate replenishment tasks overnight. Picker downtime waiting for replenishment decreased 94%.
8. Cross-Docking Workflows
What is cross-docking workflow?
Cross-docking workflow receives inbound products and immediately transfers them to outbound shipments without intermediate storage. This eliminates putaway and picking steps for qualifying products.
Cross-Docking Workflow Process:
Receive advance shipping notice with product details. Coordinate inbound and outbound schedules. Receive products at dock door. Sort products by destination immediately. Move directly to outbound staging area. Load onto outbound trucks for delivery.
Benefits of cross-docking workflows:
Reduces handling costs by eliminating putaway and picking. Accelerates product flow through warehouse. Minimizes warehouse space requirements for cross-docked items.
A Georgia food distributor cross-docks 35% of inbound volume directly to retail store deliveries. This warehouse workflow reduces handling costs $0.85 per case while accelerating delivery by 1-2 days.
Want to explore which warehouse workflows offer the biggest automation opportunity for your operation? Contact our logistics automation team to discuss workflow assessment and optimization strategies.
Understanding Warehouse Barcode Systems: Foundation of Modern Workflows
Before automating complex warehouse workflows, you need accurate data capture. Warehouse barcode scanning provides the foundation for every automated workflow by creating digital records of physical inventory movements.
What is a Warehouse Barcode System?
A warehouse barcode system assigns unique identifiers to inventory items, storage locations, and equipment, enabling automatic tracking through digital scanning rather than manual data entry. When warehouse staff scan these barcodes using handheld devices, your warehouse management system updates automatically with real-time location and quantity data.
According to research on barcode technology, warehouse barcode scanning eliminates 99%+ of manual data entry errors, provides instant inventory visibility across facilities, enables real-time tracking of product movements, supports automated reordering and cycle counting, and creates complete audit trails for compliance requirements.
Types of Warehouse Barcodes
Different warehousing scenarios require different barcode approaches:
1D Linear Barcodes (Traditional Barcodes)
These familiar horizontal bars work well for basic inventory tracking. Common formats include Code 128, Code 39, and UPC/EAN for retail products. 1D warehouse barcodes store limited information but scan reliably even with older equipment and work on small label spaces.
2D Matrix Barcodes (QR Codes & Data Matrix)
2D warehouse barcodes store significantly more data in smaller spaces. A single QR code can contain product details, lot numbers, expiration dates, serial numbers, and handling instructions. Warehouses handling complex products with extensive attributes benefit from 2D barcode systems.
RFID Tags (Radio Frequency Identification)
While technically not visual barcodes, RFID represents the next evolution in automatic identification. RFID enables scanning multiple items simultaneously without line-of-sight requirements, reading through packaging and containers, longer read ranges than traditional barcodes, and automated inventory verification without manual scanning.
A New Jersey pharmaceutical distributor implemented comprehensive warehouse barcode scanning across all inventory locations and equipment. Before barcode implementation, inventory accuracy hovered at 87% with frequent picking errors. After deployment, accuracy improved to 99.2% and picking errors decreased 73%.
The lesson: Accurate data capture through warehouse barcode systems precedes successful workflow automation.
Implementing Warehouse Barcode Scanning in Your Workflows
Successful warehouse barcode scanning requires more than buying scanners and printing labels. Strategic implementation across all warehouse workflows delivers maximum value.
Step 1: Standardize Location Barcoding
Before labeling inventory, create a logical location hierarchy for your warehouse. Use consistent naming conventions:
Aisle-Bay-Shelf-Bin formats like A1-B3-S2-01. Zone-Row-Position formats like Z1-R15-P08. Warehouse-Zone-Location for multi-facility operations.
Print durable warehouse location barcodes for every storage position. When putaway staff scan location barcodes during storage, your WMS records exact placement automatically, enabling perfect picking accuracy.
Step 2: Choose Scanning Hardware for Your Workflows
Match devices to workflow requirements:
Stationary scanners for receiving and shipping stations where products come to fixed positions.
Handheld scanners give picking and putaway staff mobility throughout the warehouse.
Wearable ring scanners enable hands-free scanning during physical handling, ideal for picking workflows.
Voice-directed systems with barcode verification combine hands-free guidance with scan verification for maximum accuracy.
A Michigan food distributor equipped order pickers with ring scanners integrated to voice-directed picking systems. This warehouse barcode scanning combination improved pick rates 40% while maintaining 99.7% accuracy.
Our enterprise software development capabilities include building custom barcode integration that connects scanning hardware with your specific WMS and workflow requirements.
Step 3: Integrate Barcode Workflows Across All Processes
Warehouse barcode scanning generates valuable data that multiple systems and workflows need:
Receiving workflows scan inbound products to verify against purchase orders and create inventory records.
Putaway workflows scan products and locations to record exact storage positions.
Picking workflows scan items during selection to verify accuracy and update inventory.
Packing workflows scan finished orders to confirm contents and generate shipping labels.
Cycle counting workflows scan locations and products to verify inventory accuracy.
Shipping workflows scan packages to confirm carrier assignments and create manifests.
A California third-party logistics provider integrated warehouse barcode data across client ERP systems, generating automatic shipment notifications and inventory updates without manual data export or re-entry.
Step 4: Train Staff on Barcode Workflow Best Practices
Technology only works when people use it correctly. Train warehouse teams to:
Scan every item at every workflow stage to maintain data integrity. Verify scans visually before proceeding to next task. Report damaged or illegible warehouse barcodes immediately. Understand how scanning discipline impacts entire operation. Never manually enter data that should be scanned.
A Pennsylvania automotive parts warehouse discovered that 15% of picking errors occurred when staff manually entered quantities instead of scanning. Reinforcing scan-every-item discipline reduced errors 82%.
Step 5: Monitor Barcode Workflow Performance
Track metrics revealing barcode system effectiveness:
Scan compliance rate: percentage of required scans completed. Scan error rate: invalid or duplicate scans requiring correction. Barcode label quality: damaged or unreadable labels needing replacement. Workflow completion time: process speed with barcode scanning versus manual methods.
Regular monitoring identifies issues before they cascade into operational problems.
Ready to implement warehouse barcode systems that actually improve your workflows? Explore our warehouse automation solutions to discover implementation strategies matched to your facility.
The Benefits of Demand Forecasting in Warehouse Management Workflows
Accurate demand forecasting transforms warehouse operations from reactive firefighting to proactive optimization, impacting nearly every workflow throughout your facility.
What is Demand Forecasting in Warehouse Management?
Demand forecasting is the process of predicting future customer demand for products using historical data, statistical algorithms, and market intelligence. In warehouse management context, demand forecasting enables proactive inventory positioning, optimal staffing levels, and efficient space allocation.
Key Benefits of Demand Forecasting for Warehouse Workflows
Understanding the benefits of demand forecasting helps justify investment in predictive analytics and AI-powered planning tools:
Benefit 1: Optimized Inventory Levels Throughout Workflows
Demand forecasting prevents both stockouts that disrupt picking workflows and overstock that wastes warehouse space and working capital. Forecasting algorithms analyze historical demand patterns, seasonal trends, promotional impacts, and external factors to predict future requirements accurately.
With accurate forecasts, receiving workflows bring in the right products at the right time, putaway workflows allocate optimal storage space, picking workflows always have products available, and replenishment workflows prevent stockouts proactively.
Benefit 2: Improved Labor Planning and Workflow Capacity
Labor represents 50-70% of warehouse operating costs. Demand forecasting enables staffing appropriately for forecasted volume rather than scrambling for temporary workers during unexpected surges or paying idle staff during slow periods.
Forecast-driven labor planning ensures receiving workflows have adequate dock staff when shipments arrive, picking workflows have sufficient pickers for order volumes, packing workflows maintain throughput without bottlenecks, and shipping workflows close manifests on schedule.
Benefit 3: Enhanced Space Utilization Across Workflows
Demand forecasting reveals which products will require significant warehouse space in coming weeks, enabling proactive space allocation. Seasonal products move to forward picking positions before demand peaks. Slow-moving inventory consolidates to deep storage areas, freeing prime locations for faster movers.
Benefit 4: Reduced Holding Costs Through Faster Inventory Turns
When inventory levels match demand accurately, products move through warehouse workflows faster. Reduced cycle time means lower holding costs, less risk of obsolescence, and improved cash flow.
Benefit 5: Better Customer Service Through Consistent Availability
Customers receive faster delivery when demand forecasting ensures products remain in stock. Picking workflows execute without backorder delays, and shipping workflows dispatch complete orders on schedule.
According to supply chain research, companies implementing advanced demand forecasting reduce inventory carrying costs by 15-30% while improving in-stock rates by 5-10%.
Real-World Demand Forecasting Benefits Example
A Pennsylvania outdoor equipment distributor implemented AI-powered demand forecasting integrated with their warehouse management workflows:
Before forecasting: 42 days average inventory on hand. 91% in-stock rate with frequent stockouts. Emergency freight costs for rush replenishment: $125,000 annually. Excess inventory write-downs: $78,000 annually.
After implementing demand forecasting: 33 days average inventory on hand (22% reduction). 97% in-stock rate with minimal stockouts. Emergency freight costs: $31,000 annually (75% reduction). Excess inventory write-downs: $12,000 annually (85% reduction).
Total annual savings: $160,000 plus improved customer satisfaction.
The warehouse operated more efficiently with less inventory because demand forecasting enabled stocking precisely what customers would order.
Implementing Demand Forecasting in Warehouse Workflows
Effective demand forecasting requires quality data, appropriate algorithms, and integration with warehouse operations.
Collect Comprehensive Historical Data
Demand forecasting accuracy depends on data quality. Gather minimum 24 months of historical sales by SKU, promotional calendars and discount periods, pricing history and competitive factors, seasonal patterns and holiday impacts, and external factors affecting demand like weather or economic trends.
Choose Forecasting Methods Matched to Products
Different products require different forecasting approaches:
Statistical forecasting works well for products with stable, predictable demand. Simple moving averages or exponential smoothing often suffice.
Machine learning forecasting handles complex demand patterns influenced by multiple variables. These algorithms identify non-obvious correlations improving prediction accuracy.
Collaborative forecasting incorporates input from sales teams, suppliers, and customers when algorithmic approaches prove insufficient.
For warehouse operations with diverse product portfolios, our AI development services build custom forecasting models handling product variety and complexity.
Integrate Forecasts into Warehouse Workflows
Demand forecasting delivers value when integrated into operational decisions:
Receiving workflows schedule inbound shipments based on forecasted demand timing. Putaway workflows allocate storage locations anticipating pick frequency. Replenishment workflows trigger based on forecasted consumption rather than just current stock levels. Labor planning schedules warehouse staff matching predicted workload.
A New York specialty foods distributor connected demand forecasts directly to warehouse management workflows. The system automatically adjusted slotting strategies monthly, moving seasonal products to accessible locations two weeks before demand peaks.
Curious how demand forecasting could transform your warehouse efficiency? Schedule a consultation to explore forecasting strategies for your specific operation.
How to Map and Document Warehouse Management Workflows
Before automating or optimizing warehouse operations, thoroughly document current workflows showing how work actually flows through your facility.
Why Map Warehouse Workflows?
A Georgia electronics distributor purchased a sophisticated warehouse management system based on vendor demonstrations. Implementation stalled when they discovered their actual receiving workflow bore no resemblance to the "standard" workflows the software assumed.
After halting implementation, spending three weeks mapping real workflows, and customizing the system accordingly, they successfully deployed automation reducing receiving time 38%.
The lesson: Automate reality, not theoretical processes.
How to Document Warehouse Workflows Step-by-Step
Step 1: Shadow Operations Across Multiple Shifts
Workflow varies significantly between day and night shifts, weekday and weekend operations, peak and slow periods. Map workflows during different conditions to understand full operational reality.
A California food distributor discovered their night shift used completely different putaway logic than day shift because warehouse layout made different sense when forklifts had clear aisles. Mapping both revealed optimization opportunities neither shift alone would show.
Step 2: Interview Frontline Warehouse Staff
People executing workflows daily know where inefficiencies hide. Ask open-ended questions:
What part of your job consumes most time? Where do you frequently encounter problems or delays? What workarounds have you created to make processes work? If you could change one thing about current workflows, what would it be?
Our discovery methodology for warehouse projects emphasizes observing actual operations over multiple shifts and interviewing staff at all levels to capture workflow variations.
Step 3: Document Exception Handling Workflows
Standard workflows matter, but exception handling often consumes disproportionate time. Map what happens when:
Products arrive damaged or with incorrect quantities. Inventory locations are full during putaway. Picks can't be found in assigned locations. Orders require special packaging or handling. Systems go offline or scanners malfunction.
Understanding exception workflows reveals automation opportunities for managing non-standard situations.
Step 4: Create Visual Workflow Diagrams
Visual documentation helps everyone understand current state and identify improvement opportunities. Document:
Process steps in sequence with timing estimates. Decision points and branching logic. System interactions and data handoffs. Warehouse barcode scanning touchpoints. Pain points and bottleneck locations.
A Massachusetts distribution center created before-and-after workflow maps for their automation project. These visuals proved invaluable for training staff and demonstrating ROI to leadership.
Step 5: Identify Automation Opportunities
Once current workflows are documented, systematically identify where automation adds value:
High-volume repetitive tasks like manual data entry, physical item scanning, or label printing.
Data transfer between systems where staff manually move information.
Rule-based decision making that follows consistent logic.
Predictable exception scenarios that can be automated when they follow patterns.
A Texas industrial distributor identified 23 automation opportunities from workflow mapping. They prioritized based on impact and implementation complexity, tackling high-impact simple wins first for quick ROI.
Warehouse Management Workflow Automation: Technologies and Best Practices
Modern technology transforms how warehouse workflows execute, delivering efficiency improvements impossible with manual processes.
Warehouse Management System (WMS) as Workflow Engine
A warehouse management system orchestrates all facility workflows through centralized software coordinating receiving, putaway, picking, packing, shipping, and inventory management.
Core WMS Workflow Capabilities:
Task generation and assignment based on priority and resource availability. Real-time inventory tracking across all warehouse locations. Workflow routing and exception handling automation. Performance monitoring and reporting across all operations. Integration with barcode scanners, RFID, and automation equipment.
When to Implement WMS:
Your warehouse handles 50+ SKUs with regular turnover. Order volume exceeds 100 daily shipments. Inventory accuracy falls below 95%. Pick and pack errors impact customer satisfaction. You operate multiple warehouse locations requiring coordination.
For organizations evaluating warehouse management systems, our team helps assess requirements, compare solutions, and implement systems matched to your specific workflows and budget.
Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) in Warehouse Workflows
AGVs automate material movement throughout warehouse facilities, reducing labor requirements for putaway and replenishment workflows.
AGV Applications in Warehouse Workflows:
Putaway automation moves products from receiving to storage locations following WMS instructions.
Replenishment automation brings inventory from bulk storage to forward picking positions.
Goods-to-person picking delivers products to stationary pickers rather than pickers traveling warehouse aisles.
- Art
- Causes
- Crafts
- Dance
- Drinks
- Film
- Fitness
- Food
- Jocuri
- Gardening
- Health
- Home
- Literature
- Music
- Networking
- Alte
- Party
- Religion
- Shopping
- Sports
- Theater
- Wellness